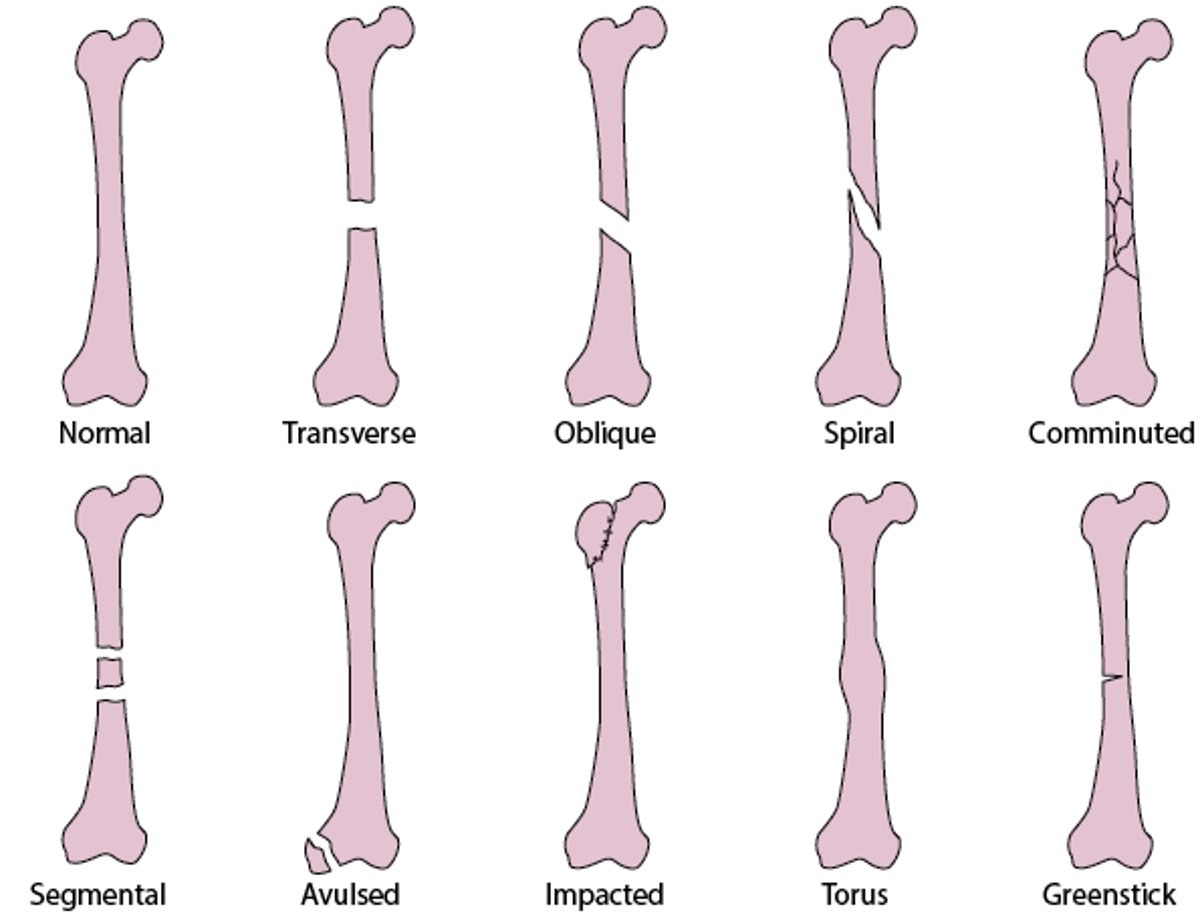
Common Types of Fracture Lines
Transverse fractures are perpendicular to the long axis of a bone.
Oblique fractures occur at an angle.
Spiral fractures result from a rotatory mechanism; on radiographs, they are differentiated from oblique fractures by a component parallel to the long axis of bone in at least 1 view.
Comminuted fractures have > 2 bone fragments. Comminuted fractures include segmental fractures (2 separate breaks in a bone).
Avulsion fractures are caused by a tendon dislodging a bone fragment.
In impacted fractures, bone fragments are driven into each other, shortening the bone; these fractures may be visible as a focal abnormal density in trabeculae or irregularities in bone cortex.
Torus fractures (buckling of the bone cortex) and greenstick fractures (cracks in only 1 side of the cortex) are childhood fractures.